Application to breast cancer dataset
Contents
Application to breast cancer dataset#
Prepare dataset#
Load#
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pd.options.display.max_columns = 10
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
data = load_breast_cancer()
data_X, data_y = data.data, data.target
X = pd.DataFrame(data=data_X, columns=data.feature_names)
y = pd.Series(data_y)
Create artificial categorical variable#
For illustration purposes, create a random categorical feature
X["category"] = np.where(X["mean smoothness"] <= 0.1, "A", "B")
Split train/test#
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=0
)
Create unknown category in test set#
To illustrate robustness of implementation, create unknown category in test set
X_test["category"] = "C"
Automatically create binary features#
Call EBMBinarizer#
The binary feature creation is based on train dataset.
The train and test dataset are then transformed for training and evaluation.
from scorepyo.binarizers import EBMBinarizer
binarizer = EBMBinarizer(max_number_binaries_by_features=3, keep_negative=True)
binarizer.fit(X_train, y_train, categorical_features="auto", to_exclude_features=None)
X_train_binarized = binarizer.transform(X_train)
X_test_binarized = binarizer.transform(X_test)
X_train_binarized.sample(3)
| mean radius < 12.26 | 12.26 <= mean radius < 14.66 | mean radius >= 14.66 | mean texture < 17.2 | 17.2 <= mean texture < 20.66 | ... | worst fractal dimension < 0.07 | 0.07 <= worst fractal dimension < 0.09 | worst fractal dimension >= 0.09 | category_A | category_B | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 401 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ... | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ... | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 316 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ... | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
3 rows × 92 columns
Display information from binarizer#
The binarizer also computes a dataframe containing information about the binarizing process. This information is later used to for the risk-score model.
It contains the following information for each binary feature created:
name of binary feature
log-odd coefficient of the binary feature according to EBM underlying model
lower and upper threshold value used for creating the interval on the original feature domain
category value if the original feature was categorical
original feature name
original feature type
number of samples with a positive value on this binary feature
name of the original feature
binarizer.get_info()
| log_odds | lower_threshold | upper_threshold | category_value | feature | type | density | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_feature | |||||||
| mean radius < 12.26 | 0.135708 | NaN | 12.26 | None | mean radius | continuous | 142 |
| 12.26 <= mean radius < 14.66 | 0.086529 | 12.26 | 14.66 | None | mean radius | continuous | 142 |
| mean radius >= 14.66 | -0.222237 | 14.66 | NaN | None | mean radius | continuous | 142 |
| mean texture < 17.2 | 0.740917 | NaN | 17.205 | None | mean texture | continuous | 142 |
| 17.2 <= mean texture < 20.66 | 0.056726 | 17.205 | 20.665 | None | mean texture | continuous | 142 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 0.07 <= worst fractal dimension < 0.09 | 0.372596 | 0.07428 | 0.08649 | None | worst fractal dimension | continuous | 142 |
| worst fractal dimension >= 0.09 | -0.156302 | 0.08649 | NaN | None | worst fractal dimension | continuous | 142 |
| category_A | 0.192341 | None | None | A | category | categorical | 266 |
| category_B | -0.319767 | None | None | B | category | categorical | 160 |
| intercept | 1.367172 | None | None | None | intercept | None | None |
93 rows × 7 columns
Train RiskScore model#
The RiskScore models can take several parameters divided into three sets:
Binarizer parameter :
binarizer: binarizer to use for the risk score model
Risk score cards parameters : defines the property of the score card
nb_max_features: number of maximum binary features to use for the risk score modelmin_point_value: minimum possible number of points for each binary featuremax_point_value: maximum possible number of points for each binary feature
Exploration/fitting parameters : defines the different exploration phase of the risk score model
ranker: ranker of binary featuresnb_additional_features: number of additional features to take into the subset of binary features according to the rankerenumeration_maximization_metric: maximization metric that will be used to elicit the best enumerated combinationcalibrator: calibrator of probabilities for each score
EBMRiskScore is a child class of RiskScore, that automatically uses EBMBinarizer as a binarizer.
from scorepyo.models import EBMRiskScore
scorepyo_model = EBMRiskScore(
nb_max_features=4,
min_point_value=-1,
max_point_value=2,
)
scorepyo_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
<scorepyo.models.EBMRiskScore at 0x1f8437cdc40>
Display the summary of the risk score model#
The summary of the risk score built by the model.
It displays two elements :
Feature-point card : Points for each selected binary feature
Score card : Scores (=sum of points) with their associated probability
scorepyo_model.summary()
======================
| FEATURE-POINT CARD |
======================
| Feature | Description | Point(s) | |
|:---------------------|:-----------------------------|:-----------|:------|
| worst concave points | worst concave points >= 0.14 | -1 | ... |
| area error | area error >= 33.35 | -1 | + ... |
| worst radius | worst radius >= 16.66 | -1 | + ... |
| worst texture | worst texture < 22.66 | 1 | + ... |
| | | SCORE= | ... |
=======================================
=======================================
======================
| SCORE CARD |
======================
| SCORE | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
|:--------|:------|:------|:-------|:-------|:-------|
| RISK | 0.00% | 2.50% | 46.15% | 95.83% | 99.10% |
Evaluation on test set#
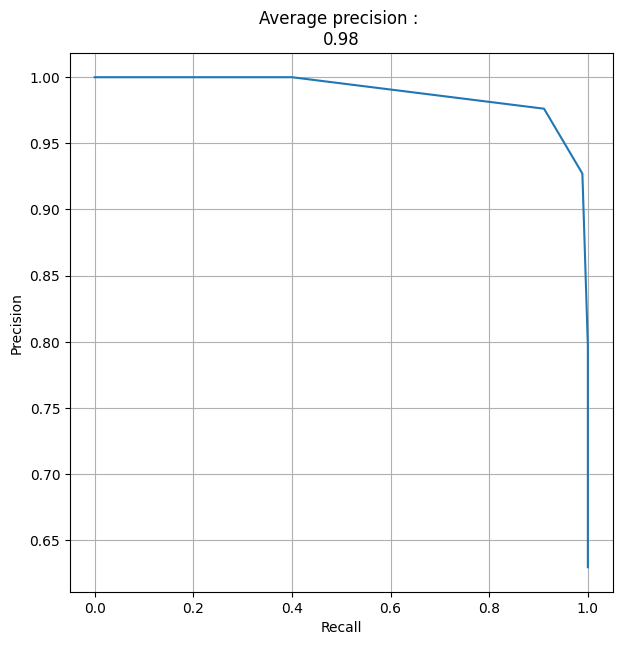
Precision-Recall curve on test set#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve, average_precision_score
y_proba = scorepyo_model.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1].reshape(-1, 1)
precision, recall, thresholds = precision_recall_curve(y_test.astype(int), y_proba)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7))
plt.plot(recall, precision)
average_precision = np.round(average_precision_score(y_test.astype(int), y_proba), 3)
title_PR_curve = f"Average precision : \n{average_precision}"
plt.title(title_PR_curve)
plt.xlabel("Recall")
plt.ylabel("Precision")
plt.grid()
plt.show()